For May, it’s in your bones: calcium and phosphorus
The International Year of the Periodic Table marks the 150th anniversary of Dimitri Mendeleev’s periodic system. The 91—«…´¥´√Ω is joining the celebration with a series of articles on biochemical elements. Since January, we have presented hydrogen; iron; sodium, potassium and chlorine; and copper.
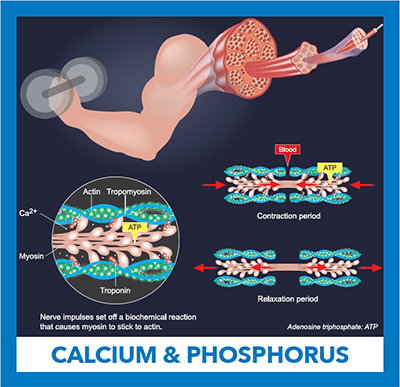 An electrical impulse traveling from a motor neuron results in the release of calcium from the muscle’s intracellular stores. Ca+2 binds to the inhibitory troponin-tropomyosin complex, allowing myosin and actin filaments to slide past one another causing muscle contraction. Adenosine triphosphate is hydrolyzed in the process. Relaxation follows when cytoplasmic calcium is removed.
An electrical impulse traveling from a motor neuron results in the release of calcium from the muscle’s intracellular stores. Ca+2 binds to the inhibitory troponin-tropomyosin complex, allowing myosin and actin filaments to slide past one another causing muscle contraction. Adenosine triphosphate is hydrolyzed in the process. Relaxation follows when cytoplasmic calcium is removed.
May is arthritis awareness month, so we selected calcium and phosphorous, the two components of the mineral salt hydroxyapatite that makes up about 65 percent of the human .
With chemical symbol Ca and atomic number 20, calcium is classified in the periodic table as an alkaline earth metal. In chemical reactions, calcium easily loses the two valence electrons in its outermost orbital to form ionic compounds that contain dipositive Ca+2.
At 3 percent of the Earth crust’s mass, calcium is the fifth most abundant element and the third most common metal after iron and aluminum. Most of the Earth’s calcium is found as a carbonate mineral in limestone — sedimentary rock that contains fossilized sea life. Calcium carbonate makes corals, sea shells and pearls when Ca+2 released by weathering reacts with seawater bicarbonate.
Calcium is essential in biology. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes maintain low intracellular free Ca+2 via ion channels, transporters and calcium-sequestering proteins. In response to environmental changes, intracellular Ca+2 rapidly rises, transmitting the outside information to the interior of the cell. In bacteria, this regulates chemotaxis — or movement toward a chemical stimulus — and flagellar rotation.
In mammals, cells respond to hormones by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathway that leads to high intracellular Ca+2 and expression of calcium-dependent genes. Excited neurons release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which binds to its receptor on the receiving cell, opening ion channels and allowing the influx of extracellular Ca+2. At synapses, the inflow of calcium propagates the electrical signal to the receiving neuron, and at neuromuscular junctions, it triggers muscle contraction in the receiving fiber.
Phosphorus — with chemical symbol P and atomic number 15 — is a reactive nonmetal that combines with other elements mainly by sharing electrons via covalent bonds. Free phosphorus is rare; the element normally is found in compounds in oxidation states of +3, +5 and -3.
Phosphorus is the 11th most common element on Earth. About one gram of phosphate is found for every kilogram of the Earth’s crust, mostly in the form of oxidized inorganic rocks formed over millions of years.
. Some bacteria derive energy for growth by oxidizing H2PO3– or phosphite to inorganic phosphate. Phosphate groups are major structural components of nucleotides, which are the building blocks for nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. Phospholipids — which contain a hydrophobic fatty acid “tail” and a hydrophilic phosphate “head” — form lipid bilayers that constitute cellular membranes.
Most cellular metabolic reactions are driven by chemical energy harnessed from the cleavage of adenosine triphosphate, a molecule that contains a sugar, a nitrogenous base and three phosphate groups. The addition of phosphoryl groups to proteins during phosphorylation changes protein activity and/or cellular localization, regulating a plethora of cell-signaling events.
A year of (bio)chemical elements
Read the whole series:
For January, it’s atomic No. 1
For February, it’s iron — atomic No. 26
For March, it’s a renal three-fer: sodium, potassium and chlorine
For April, it’s copper — atomic No. 29
For May, it’s in your bones: calcium and phosphorus
For June and July, it’s atomic Nos. 6 and 7
Breathe deep — for August, it’s oxygen
Manganese seldom travels alone
For October, magnesium helps the leaves stay green
Enjoy reading 91—«…´¥´√Ω Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from 91—«…´¥´√Ω Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Bacterial enzyme catalyzes body odor compound formation
Researchers identify a skin-resident Staphylococcus hominis dipeptidase involved in creating sulfur-containing secretions. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.

Neurobiology of stress and substance use
MOSAIC scholar and proud Latino, Bryan Cruz of Scripps Research Institute studies the neurochemical origins of PTSD-related alcohol use using a multidisciplinary approach.

Pesticide disrupts neuronal potentiation
New research reveals how deltamethrin may disrupt brain development by altering the protein cargo of brain-derived extracellular vesicles. Read more about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics article.

A look into the rice glycoproteome
Researchers mapped posttranslational modifications in Oryza sativa, revealing hundreds of alterations tied to key plant processes. Read more about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics paper.

Proteomic variation in heart tissues
By tracking protein changes in stem cell–derived heart cells, researchers from Cedars-Sinai uncovered surprising diversity — including a potential new cell type — that could reshape how we study and treat heart disease.

Parsing plant pigment pathways
Erich Grotewold of Michigan State University, an 91—«…´¥´√Ω Breakthroughs speaker, discusses his work on the genetic regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis.

